M-1 Volna
NATO: SA-N-1 Goa
Overview
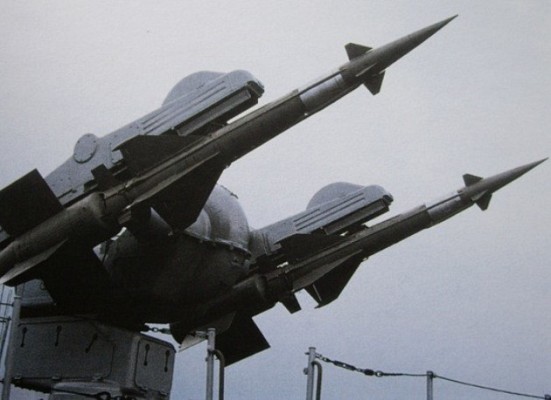

M-1 Volna
Twin arm launcher of the M-1 Volna naval SAM system.
Source: www.oruzhie.info -
© Copyright lies with original owner
4K90 (GRAU index for Volna)
4K91 (GRAU index for Volna-M)
India
Description
Introduction
The M-1 Volna is an early Cold War era naval SAM system of Soviet origin. The NATO reporting name for this system is SA-N-1 Goa. It was the first operational Soviet naval surface to air missile system providing area air defense and a degree of protection from inbound anti-ship missiles. Although combat effectiveness wasn't spectacular, in Soviet service the M-1 Volna had a reputation of good reliability.
Design
The design of the M-1 Volna is derived from the land based S-125 (NATO: SA-3 Goa). The M-1 uses a twin rail launcher with a reloading system below deck. Fire control is provided by an integrated set of radars known as 4R90 Yatagan. Target acquisition is done by the ship's radar systems. These include the 300 km range MR-500 Kliver (NATO: Big Net) and 130 km range MR-310 Angara (NATO: Head Net) surveillance and target acquisition radars.
Guidance
The M-1 Volna uses radio frequency command guidance. The 4R90 Yatagan (NATO: Peel Group) radar is derived from the land based SNR-125 and directs one or two missiles towards a single target at a time. In upgraded systems the 9Sh33 optronic director is added for use in scenarios with a high level of electronic countermeasures. The optronic director also allows for use of the missiles against surface targets.
Firepower
The M-1 Volna uses the same missiles as used on the land based variant. Early models used the V-600 with a 4 to 15 km range and 0.1 to 10 km altitude. Upgraded models use the V-601 series of surface to air missiles. These have a more powerful warhead, longer range of over 20 km and improved accuracy at lower altitude.
System composition

Surface to air missile
The M-1 Volna system uses the V-600 and V-601 series of surface to air missiles. The V-600 is used with the M-1 Volna. The improved V-601 is used with the M-1M Volna-M. The V-601P is used with the Volna-P variant, while the V-601M is used with the anti-sea skimming upgrade of the Volna-N system.
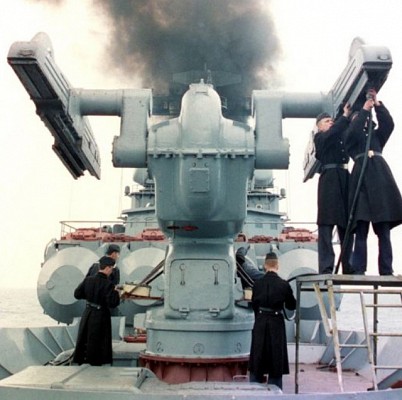

Missile launcher
Each M-1 Volna system has a single twin rail launcher. Reloading is automated and for reloading the launcher rotates to the reload position. The rails are raised into the vertical position and new missiles are hoisted onto the rails through hatches in the deck. The ZIF-101 was the first model to be introduced. It has 16 spare missiles in the below deck loading system. The ZIF-102 was introduced later and is externally similar, but has 32 reloads below deck.
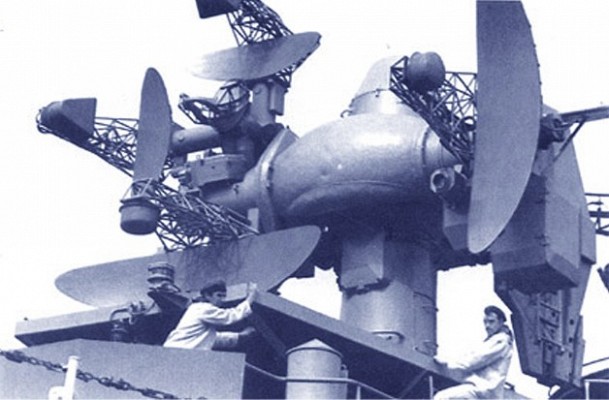
Fire control radar
Each M-1 Volna system has a single set of fire control radars. The set of five radars is known as the 4R90 Yatagan and provides target tracking and radio command guidance for the missiles. The Yatagan is the naval equivalent of the SNR-125 radar set used by the land based system.
Variants
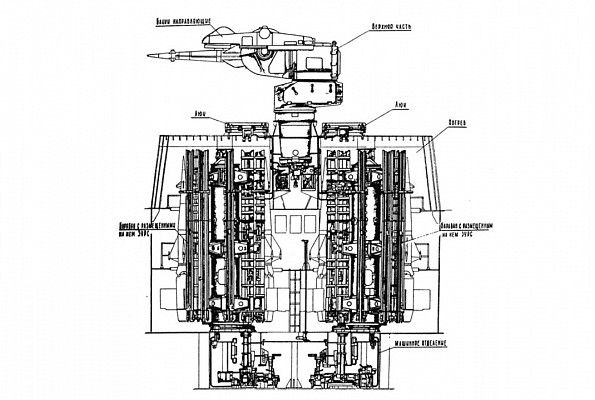
ZIF-101
Line diagram of ZIF-101 twin arm launcher showing below deck twin rotating magazine.
Source: A.B. Shikorad -
© Copyright lies with original owner
Variants of the M-1 Volna
Ship classes with Volna system
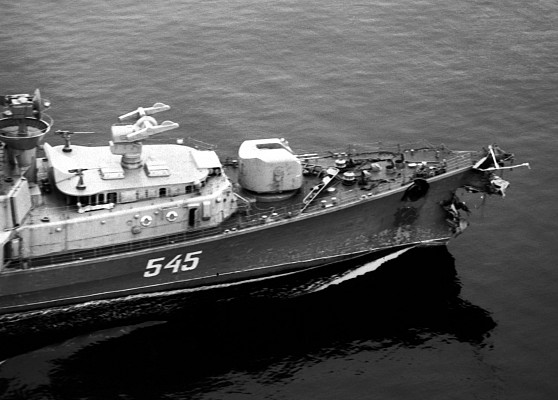

M-1 Volna
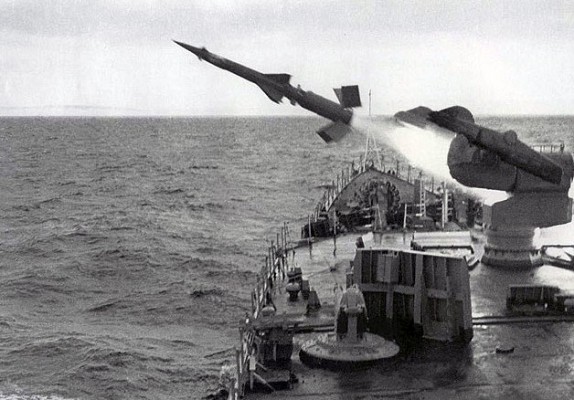
ZIF-101 launcher on a Project 61 (NATO: Kashin) class destroyer in 1986.
Source: US Navy -
© Public domain
List of ship classes with Volna system
Related articles

S-125 Neva
The M-1 Volna is the naval adaptation of the land based S-125 Neva (NATO: SA-3 Goa) surface to air missile system.

M-11 Shtorm
The M-11 Shorm (NATO: SA-N-3 Goblet) was developed as a longer range and more accurate alternative to the M-1 Volna system.